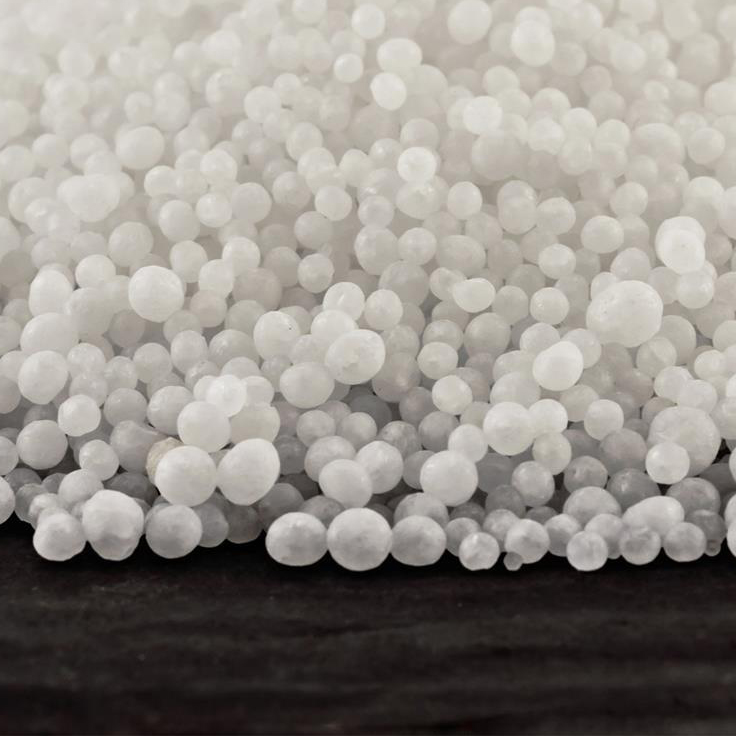
Urea fertilizer is one of the most commonly used nitrogen fertilizers in agriculture. It is a highly concentrated form of nitrogen, containing about 46% nitrogen by weight, which makes it efficient and economical for promoting plant growth.
Key Properties of Urea:
1. High Nitrogen Content: Urea has a nitrogen (N) content of 46%, which is higher than most other fertilizers.
2. Solubility: It is highly water-soluble, making it easily accessible to plants when applied properly.
3. Form: Urea comes in solid form, either as granules or crystals, and can be applied directly to the soil or dissolved in water for foliar application.
4. Cost-Effective: Its high nitrogen concentration reduces transportation and application costs per unit of nitrogen compared to other forms of fertilizers.
Application and Use:
– Soil Application: Urea can be applied directly to the soil, but it must be properly incorporated into the soil to minimize nitrogen loss through volatilization (loss of nitrogen to the atmosphere in the form of ammonia gas).
– Foliar Application: It can also be dissolved in water and sprayed onto plant leaves for a quick nutrient uptake.
– Slow-Release Forms: In some cases, urea is treated with chemicals to slow down its release, allowing a more controlled nitrogen supply over time.
Benefits:
– Promotes Plant Growth: The nitrogen in urea is vital for plant growth, promoting healthy leaf development and boosting photosynthesis.
– Versatile: It can be used on a wide range of crops, including cereals, vegetables, and fruits.