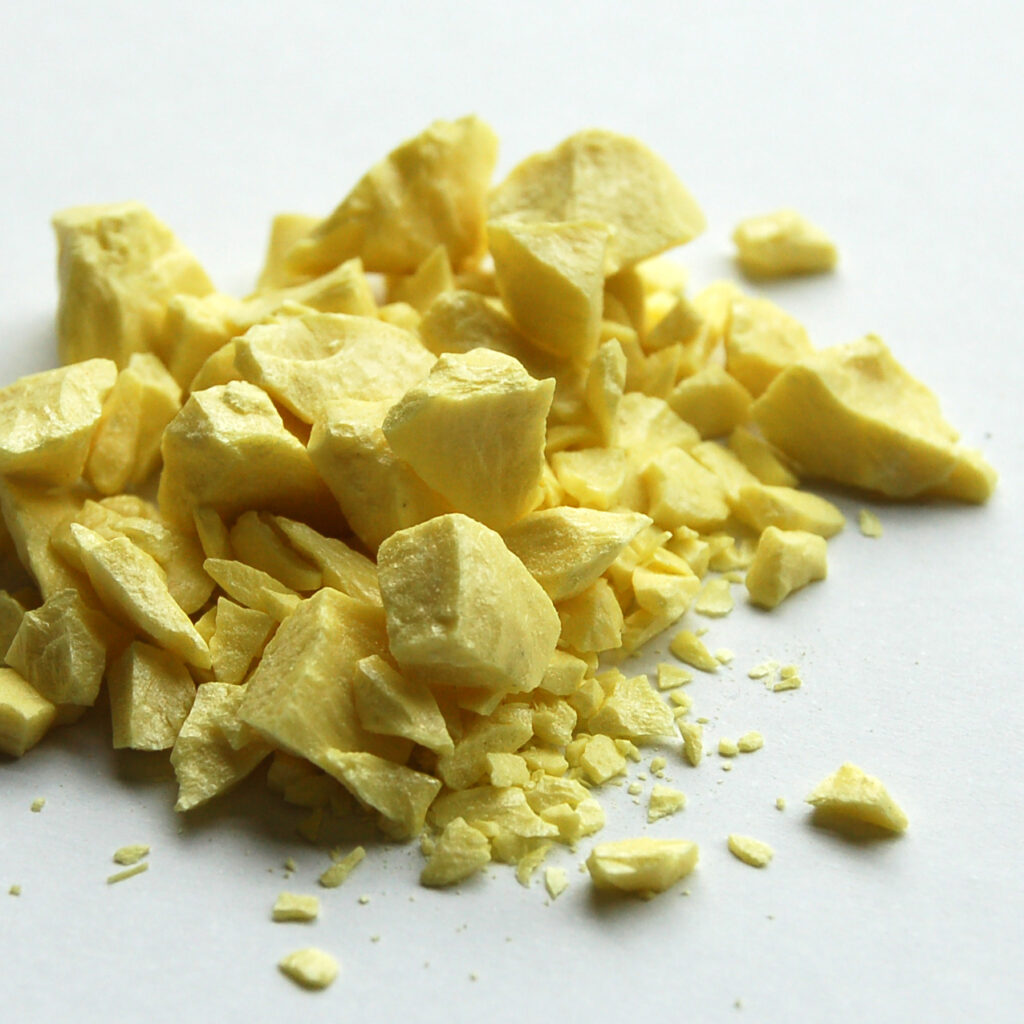
Sulfur is a chemical element with the symbol “S” and atomic number “16”. It is a non-metal, abundant in the Earth’s crust and atmosphere, and is essential for life. Sulfur appears in yellow crystalline form and is insoluble in water. It can also exist in other allotropic forms, including amorphous and liquid states.
Key Properties:
– Atomic number: 16
– Atomic mass: 32.06 g/mol
– Melting point: 115.21°C (239.38°F)
– Boiling point: 444.6°C (832.3°F)
– Density: 2.07 g/cm³
– Common oxidation states: -2, +4, +6
Uses:
– Industrial Applications: Sulfur is primarily used in the production of sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄), which is crucial in fertilizers, chemicals, and petroleum refining.
– Agriculture: It is essential in fertilizers and pesticides.
– Medicine: Sulfur is used in skin ointments and in the treatment of acne and other skin conditions.
– Food: Sulfur dioxide (SO₂) is a preservative used in food and beverages.
Natural Occurrence:
– Sulfur is found naturally near volcanic regions and hot springs. It can also be found in meteorites, ores like pyrite (FeS₂), and in the Earth’s atmosphere, where it contributes to the sulfur cycle through volcanic eruptions and the burning of fossil fuels.