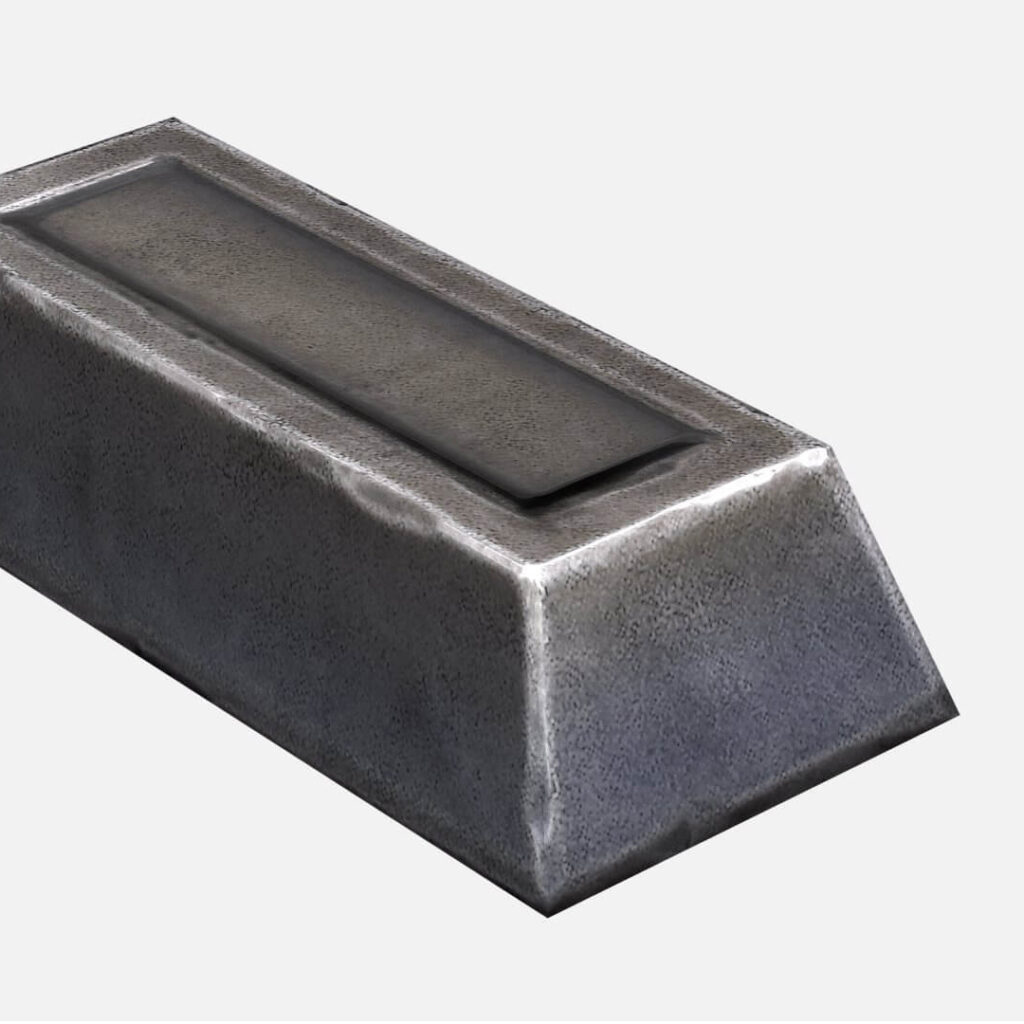
A steel ingot is a large, solid block of steel that is cast from molten metal, typically in a mold. Ingots serve as a starting material for further processing, such as rolling, forging, or extrusion, which will shape the steel into finished products like bars, sheets, or other forms.
Key Characteristics:
– Size & Shape: Ingots come in various sizes and shapes, depending on their intended use and the method of casting. Common shapes include rectangular, square, or cylindrical forms.
– Production: Molten steel is poured into molds and allowed to cool and solidify into ingots. This process is usually done in steel plants using basic oxygen furnaces or electric arc furnaces.
– Purpose: Steel ingots are used as intermediate products in the production of various steel materials. They can be re-melted, rolled, or otherwise processed into desired shapes for industrial applications.
Applications:
– Manufacturing: Steel ingots are further processed to create construction materials (e.g., beams, rods), automotive parts, machinery, and other industrial components.
– Alloy Steel: Ingots can be made from different steel alloys depending on the desired properties, such as hardness, ductility, or resistance to corrosion.