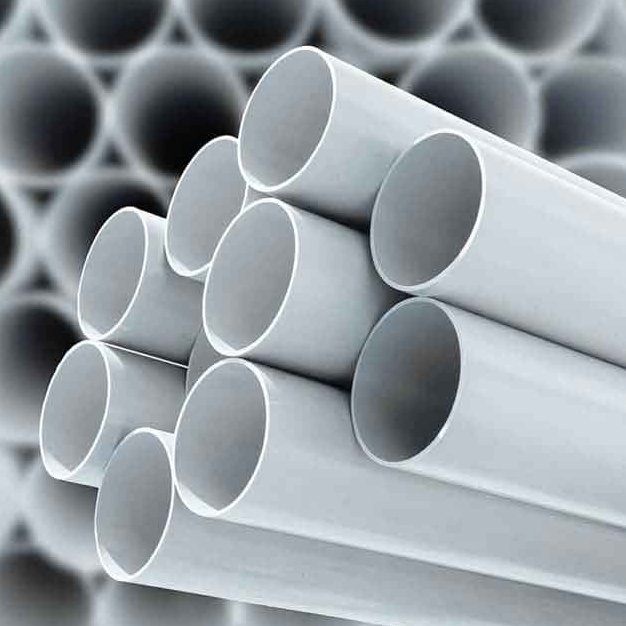
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) gfis a synthetic plastic polymer made from the polymerization of vinyl chloride monomers (C₂H₃Cl). It is one of the most commonly produced plastics in the world, known for its versatility, durability, and cost-effectiveness. PVC comes in two main forms: rigid and flexible, each with its own range of applications.
Types of PVC:
1. Rigid PVC (RPVC or uPVC – Unplasticized PVC):
– Tough, durable, and more resistant to chemicals.
– Used for construction materials like pipes, windows, and doors.
– Common in plumbing, sewage, and industrial applications.
2. Flexible PVC:
– Made by adding plasticizers (such as phthalates), which make the material softer and more flexible.
– Used in products like hoses, electrical cable insulation, flooring, and medical devices.
Key Properties of PVC:
– Durable: PVC is resistant to weathering, rotting, and corrosion, making it suitable for long-lasting applications, especially outdoors.
– Chemical Resistance: It is resistant to most acids, bases, salts, and some solvents.
– Fire Resistance: PVC has good fire-resistant properties, with a high ignition temperature and self-extinguishing nature.
– Water Resistance: It is highly resistant to moisture and water, making it ideal for pipes and water-related applications.
– Inexpensive: PVC is one of the most affordable plastics, making it popular in various industries.
– High Strength: Rigid PVC is strong, though lightweight.
Common Applications:
1. Pipes and Fittings: PVC is most widely recognized for its use in plumbing and sewage pipes. It is also used for irrigation systems, conduits, and other pipework because of its water resistance and durability.
2. Construction Materials:
– Windows and doors: Rigid PVC (uPVC) is often used for window frames and doors due to its weather resistance and insulating properties.
– Roofing membranes: It is used as a waterproofing material in construction.
3. Electrical Cable Insulation: PVC is widely used as insulation for electrical cables due to its good insulating properties and flexibility.
4. Medical Devices: Flexible PVC is used in products like blood bags, tubing, and IV containers. Its flexibility and ability to be sterilized make it ideal for these applications.
5. Flooring and Wall Coverings: PVC is used in vinyl flooring and wall coverings due to its easy-to-clean surface and moisture resistance.
6. Clothing and Upholstery: Flexible PVC can be used to create synthetic leather, raincoats, and upholstery fabrics.
7. Packaging: It can be used for packaging films, especially in products like shrink wraps.
Advantages of PVC:
– Cost-effective: One of the most affordable plastic materials available.
– Durable and long-lasting: Resistant to corrosion, chemicals, and environmental conditions.
– Versatile: Can be made rigid or flexible, depending on the application.
– Good Insulating Properties: Useful for electrical applications and building materials.
PVC’s balance of affordability, strength, and resistance to moisture and chemicals makes it one of the most popular plastics in industries ranging from construction to healthcare.