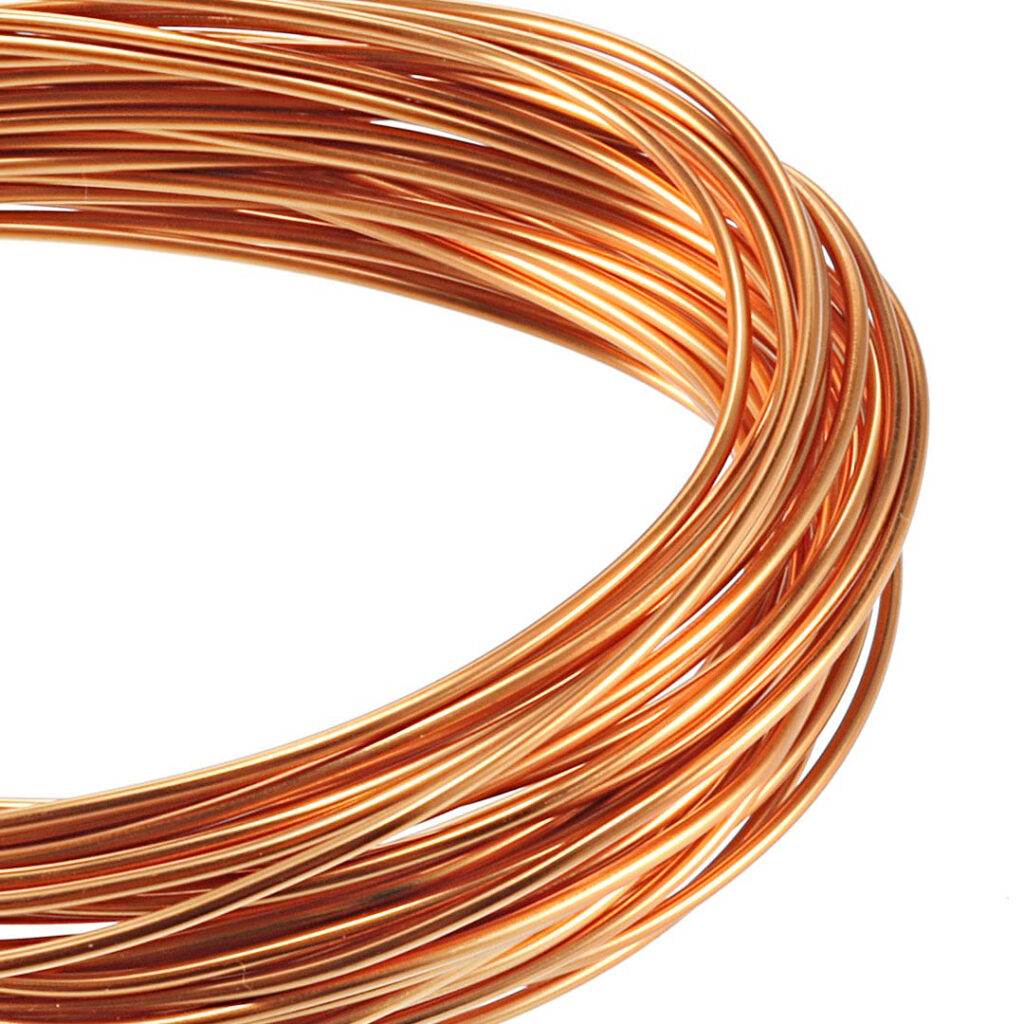
Copper wire is a widely used electrical conductor known for its excellent electrical conductivity, malleability, and ductility. Here’s a comprehensive overview of copper wire:
Types of Copper Wire
- Bare Copper Wire:
- Uninsulated wire used for grounding, electrical connections, and in various applications where insulation is not required.
- Enamelled Copper Wire:
- Also known as magnet wire, it is coated with a thin layer of insulation (typically enamel). Used in the windings of motors, transformers, and inductors.
- Insulated Copper Wire:
- Copper wire that is coated with a layer of insulation, such as PVC (polyvinyl chloride) or PE (polyethylene). Commonly used in residential and commercial electrical wiring.
- Tinned Copper Wire:
- Copper wire coated with a thin layer of tin to improve corrosion resistance. Often used in marine and outdoor applications.
- Stranded Copper Wire:
- Made from multiple small wires twisted together. More flexible than solid wire and commonly used in applications where flexibility is important.
- Solid Copper Wire:
- Made from a single solid piece of copper. Generally used for fixed installations where flexibility is not a concern.
Properties
- Conductivity: Copper is one of the best conductors of electricity, second only to silver.
- Malleability: Copper can be easily shaped and drawn into thin wires without breaking.
- Ductility: It can be stretched into wire without losing strength.
- Corrosion Resistance: Copper naturally develops a patina (greenish layer) that protects it from further corrosion.
Applications
- Electrical Wiring:
- Used in residential, commercial, and industrial buildings for power distribution and lighting.
- Electronics:
- Used in circuit boards, connectors, and various electronic components due to its conductivity.
- Telecommunications:
- Utilized in telephone lines, coaxial cables, and data transmission systems.
- Electrical Equipment:
- Used in motors, transformers, generators, and other electrical devices.
- Crafts and Jewelry:
- Used by artisans and crafters for making jewelry, sculptures, and decorative items.
Advantages
- High Conductivity: Ensures efficient electrical transmission, minimizing energy loss.
- Flexibility and Workability: Easy to handle and install, making it suitable for various applications.
- Durability: Resistant to high temperatures and corrosion, ensuring a long service life.
Conclusion
Copper wire is an essential material in the electrical and electronics industries, valued for its exceptional conductive properties and versatility. Its various forms cater to different applications, ensuring that it remains a critical component in modern technology.