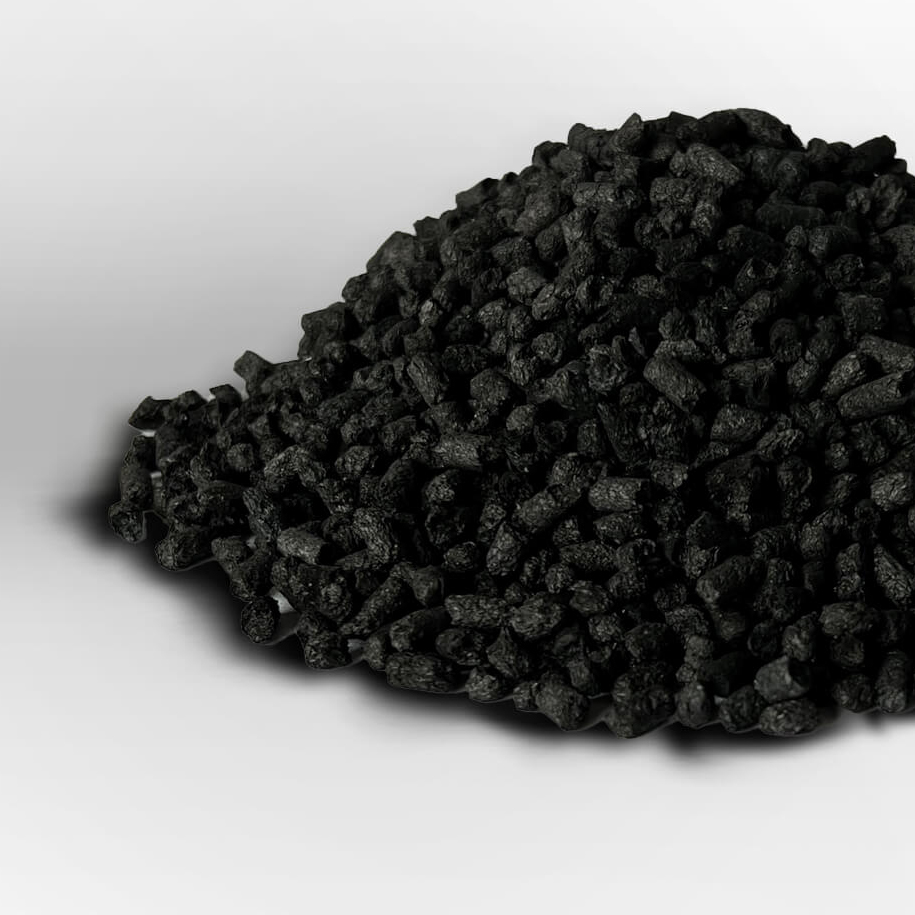
Carbon black is a fine black powder composed of elemental carbon that is produced by the incomplete combustion or thermal decomposition of hydrocarbons, such as natural gas or petroleum products. It is widely used as a reinforcing agent in rubber and a pigment in various applications, including inks, coatings, and plastics.
Key Characteristics of Carbon Black:
- Particle Size: Carbon black particles are typically very small, often in the range of 10 to 500 nanometers in diameter.
- Surface Area: Carbon black has a high surface area, which varies depending on the manufacturing process.
- Structure: The particles form complex, irregular aggregates or chains, which contribute to its reinforcing properties.
- Porosity: Many types of carbon black have a porous structure, enhancing their ability to absorb liquids or gases.
Manufacturing Processes:
- Furnace Black Process:
- The most common method for producing carbon black.
- Hydrocarbons are burned in a controlled environment with limited oxygen to produce fine carbon black particles.
- Produces a wide range of grades used for tires, rubber, and pigments.
- Thermal Black Process:
- Involves the decomposition of natural gas or other hydrocarbons in the absence of air at high temperatures.
- Produces coarser particles compared to furnace black and is mainly used in industrial rubber applications.
- Acetylene Black Process:
- Acetylene is decomposed in a controlled environment to produce very pure carbon black with high electrical conductivity.
- Used in specialized applications like batteries and conductive coatings.
- Lampblack Process:
- An older process where hydrocarbons are burned with limited oxygen to produce carbon black, traditionally used for pigments.
Types of Carbon Black:
- Reinforcing Carbon Black: Primarily used in rubber products to enhance strength, durability, and wear resistance.
- Commonly used in tires, conveyor belts, and other rubber goods.
- Pigment Carbon Black: Used in paints, inks, plastics, and coatings to provide a deep black color.
- Commonly found in printing inks, toners, plastics, and coatings for various industries.
- Conductive Carbon Black: Offers high electrical conductivity and is used in applications requiring electrostatic dissipation or conductivity, such as battery electrodes or conductive polymers.
Major Applications of Carbon Black:
- Rubber Reinforcement:
- The largest application of carbon black is in the production of tires.
- It strengthens and extends the life of rubber products by improving their resistance to wear, tear, and heat buildup.
- Carbon black provides tires with UV protection, preventing degradation from sunlight exposure.
- Pigments for Inks, Paints, and Coatings:
- Carbon black is used as a black pigment in printing inks, automotive coatings, and industrial paints.
- It provides deep black coloration, UV resistance, and opacity in formulations.
- Its small particle size ensures high tinting strength.
- Plastics and Polymers:
- Used in the manufacturing of plastic products, especially in automotive components and packaging materials.
- It provides color, UV protection, and can improve the strength of the plastic.
- Often used in cables, pipes, and films.
- Conductive Applications:
- Carbon black is used in batteries, electrical cables, and electronic devices where conductivity is required.
- Conductive carbon black is added to materials to dissipate static electricity or to improve the conductivity of battery electrodes.
- Specialized Applications:
- Carbon black is used in toners for laser printers and photocopiers.
- It is also employed in carbon black-based paints for infrared absorption or electromagnetic interference shielding.
Advantages of Carbon Black:
- Strength and Durability: Carbon black enhances the mechanical properties of rubber, making it highly valuable for tire production.
- UV Protection: It absorbs UV light, protecting materials (like tires and plastics) from degradation due to sunlight exposure.
- Versatility: Carbon black’s wide range of grades makes it suitable for diverse industries, from automotive to electronics.
- Electrical Conductivity: Conductive grades of carbon black are essential for applications where static dissipation or electrical conduction is required.