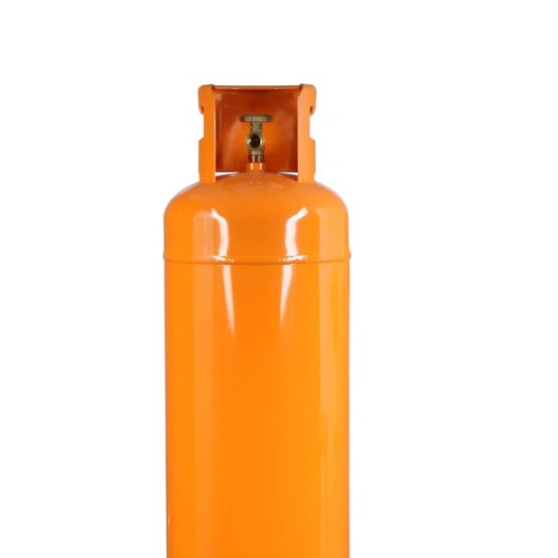
Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG) is a flammable hydrocarbon gas that is used as fuel for heating, cooking, vehicles, and other applications. It is commonly a mixture of propane and butane, which are gases under normal atmospheric conditions but can be liquefied at moderate pressure. LPG is valued for its efficiency, portability, and cleanliness compared to traditional fuels like coal or wood.
Key Characteristics of LPG:
1. Composition: LPG mainly consists of propane (C₃H₈) and butane (C₄H₁₀), often mixed in varying proportions.
2. Storage: It is stored and transported as a liquid in pressurized steel containers (cylinders or tanks) and turns back into gas when released for use.
3. Energy Efficiency: LPG has a high calorific value, meaning it provides more energy per unit compared to many other fuels.
4. Clean Burning: It produces fewer emissions compared to other fossil fuels, making it a cleaner option for heating, cooking, and vehicle use.
Applications:
1. Household Use: LPG is widely used for cooking, especially in areas without access to natural gas pipelines. It is also used for heating homes and water.
2. Industrial Use: Many industries use LPG for processes that require high heat, such as metalworking, ceramics production, and glassmaking.
3. Automotive Fuel: LPG is used as an alternative automotive fuel in many countries, often referred to as “autogas.” Vehicles running on LPG produce fewer pollutants than those running on gasoline or diesel.
4. Agriculture: It is also used in agriculture for drying crops like grains, as well as for weed control and heating greenhouses.
Advantages of LPG:
– Portability: LPG can be easily stored and transported in liquid form, making it a practical fuel in remote areas where natural gas is not available.
– Efficiency: It burns efficiently with little waste, making it a cost-effective fuel for various applications.
– Environmental Benefits: LPG produces lower greenhouse gas emissions than coal, oil, or gasoline, contributing less to air pollution and climate change.
– Versatility: It can be used for a wide range of purposes, from cooking to fueling vehicles to powering industrial machinery.
Safety Considerations:
– Flammability: LPG is highly flammable, so care must be taken in its storage and handling. Leaks can result in fires or explosions.
– Odor: Although LPG is naturally odorless, an odorant (usually ethyl mercaptan) is added so that leaks can be easily detected by smell.
– Ventilation: LPG is heavier than air, so in the event of a leak, it can accumulate in low areas, potentially creating a hazard in poorly ventilated spaces.
Environmental Impact:
– Cleaner than Fossil Fuels: While LPG is a fossil fuel, it is cleaner than other fossil fuels like coal and oil. It produces fewer sulfur, nitrogen, and particulate emissions.
Not Renewable: LPG is derived from natural gas processing and crude oil refining, so it is a non-renewable resource.
LPG is an efficient, versatile, and relatively clean fuel used in a wide variety of applications, from household cooking to large-scale industrial processes. However, it must be handled safely due to its flammability and storage requirements.